 |
DDColl utilizes RASCH chimera technology to create synthetic biologics (synbiologics ®) and GEB technology to create synthetic microbes for therapeutic purposes. Technology platforms include cell-free (CF) expression of human membrane proteins, high-speed NMR structure determination of human membrane proteins by Combinatorial Dual-isotope Labeling (CDL) technology, and accelerated Molecular Dynamics (aMD) technology to refine atomic structures and to discover lead small-molecule compounds for target proteins. |
| |
|
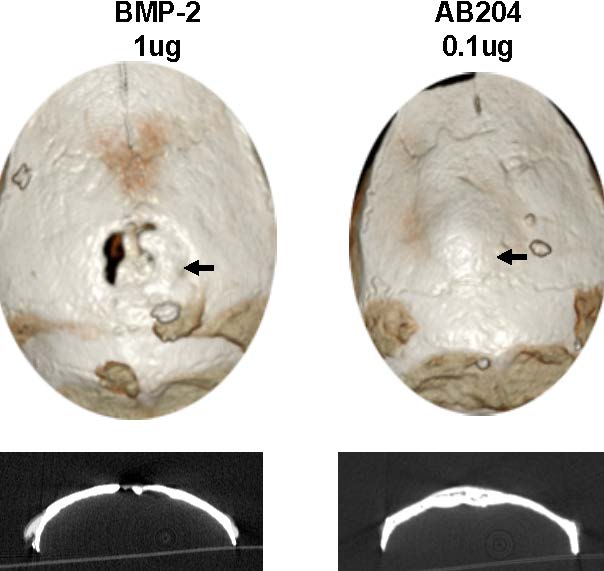 |
Random Assembly of Segmental Chimera and Heteromers (RASCH) Technology is to engineer protein messengers in the body. We aim to create novel biologics whose cell signaling capacities can go beyond those carried out by natural ones. These synthetic biologics (synbiologics ®) are used to cure diseases and also to guide stem cells' differentiation by ex vivo cell conditioning. Log in for details. |
| |
|
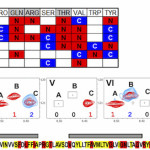 |
Combinatorial Dual-isotope Labeling (CDL) Technique: An application of the conventional NMR resonance assignment methods to the membrane proteins (and large protein systems in general) has substantial problems and limitations. Several alternative approaches based on selective isotope labeling were developed during last decade. Cell-free combinatorial Dual Labeling (CDL) approach was specifically designed to fulfill NMR assignment needs of membrane proteins. The CDL method uses amino acid sequence of the target protein to calculate the labeling scheme for maximal possible assignment of the backbone resonances. Log in for details. |
| |
|
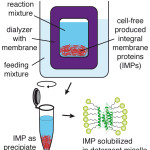 |
Cell-Free (CF) Expression of Membrane Proteins: The cell-free (CF) expression technology is based on a crude E. coli lysate, supplemented with amino acids, T7 RNA polymerase and an efficient ATP regeneration system. A dialysis membrane separates the reaction mixture, containing the transcription/translation machinery, from a feeding mixture that supplies amino acids and energy substrates to ensure preparative scale protein synthesis within incubation over night. In the absence of detergents or lipids, integral membrane proteins are produced as a pure precipitate that can be harvested by centrifugation and solubilized in appropriate detergents. Log in for details. |
| |
|
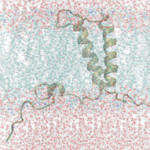 |
Accelerated Molecular Dynamics (aMD): Accelerated molecular dynamics (aMD) is an enhanced molecular modeling technique used to simulate the motions of the proteins inside the membrane. Conformations of the protein at different time points are extracted and used as input structures for computer-aided drug discovery. This procedure accounts for protein flexibility during docking. Log in for details. |
|
|
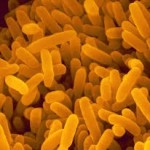 |
Genetically Engineered Bacteroides (GEB): Bacteroides are Gram-negative anaerobic microbes, residing in the human intestinal tract. It normally brings in and hydrolyzes non-digestible polysaccharides as well as an environment sensing mechanism consisting of outer membrane proteins. Geneticaclly Engineered Bacteroides (GEB) will have great importance in terms of the study of the symbiotic gut bacteria as a novel type of vaccine to combat chronic infections. Log in for details. |






 Drug Discovery Collaboratory
Drug Discovery Collaboratory